Projects
Objectives:
• Model underlying system
• Identify system constraints and bottlenecks
• Examine ahead the impact of different scenarios and plans on system performance before implementing them
• Improve patient’s throughput time (TPT)
• Propose potential improvements and developments
• Communicate and gain insights into strategic initiatives, key objectives, and actions
• Identify system constraints and bottlenecks
• Examine ahead the impact of different scenarios and plans on system performance before implementing them
• Improve patient’s throughput time (TPT)
• Propose potential improvements and developments
• Communicate and gain insights into strategic initiatives, key objectives, and actions
Description:
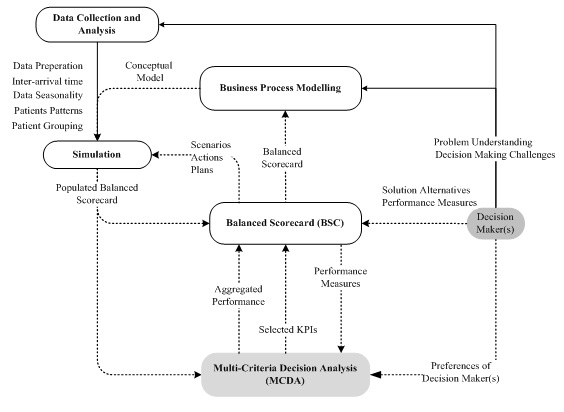
A collaborative study has been initiated between the management team of the emergency department (ED) in a University Hospital in north Dublin and 3S group at DIT. Since June 2008, the project has been progressed through different phases. The ED managers have provided historical data about patients’ arrival rate as well as about medical staff scheduling and skills. Due to some gaps in the recording data, close contact and collaboration with the staff was performed in order to measure processing times of different kinds of processes such as patient triage, diagnoses, and laboratory tests. Electronic records, direct observations, and staff interviews were the main sources for collected data. Subsequently, the collected data has been analysed to model the care path of patients presented with different medical conditions. The processes have been mapped, primarily represented on flowchart diagrams which were elaborated and detailed using standard conceptual modelling tools. Then, a comprehensive simulation model was coded to include all the details about different ED processes and to simulate the dynamics inside the ED. After that, the simulation model has been integrated with Balanced Scorecard (BSC), to track two main measures: patient satisfaction and ED efficiency. The main factors in patient satisfaction are average waiting time and cycle time where for ED efficiency came out as ED productivity and resource utilisation. The analysis of as-it-is scenario identified three observations; high waiting time at triage area, poor utilization at some treatment areas, and considerable record of patients left the hospital without treatment. Results have shown the potential of the proposed integrated framework and have reflected on potential strategies for improvement.